
SL Paper 1
Lewis structures are represented in different ways in different parts of the world. Two ways of drawing the Lewis structure for \({{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^ + }\) are shown below.

Which statement is correct about \({{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^ + }\)?
A. The ion has a tetrahedral shape.
B. The H–O–H bond angle is 120°.
C. The H–O–H bond angle is 90°.
D. The ion has a trigonal pyramidal shape.
Which compound has the lowest boiling point?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
Which is the best description of a metallic bond?
A. Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
B. Electrostatic attraction between a pair of electrons and positively charged nuclei
C. Electrostatic attraction between a lattice of positive ions and delocalized electrons
D. Electrostatic attraction for a bonding pair of electrons which have been supplied by one of the atoms
Which statements are correct about hydrogen bonding?
I. It is an electrostatic attraction between molecules.
II. It is present in liquid ammonia.
III. It is a permanent dipole-permanent dipole attraction.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
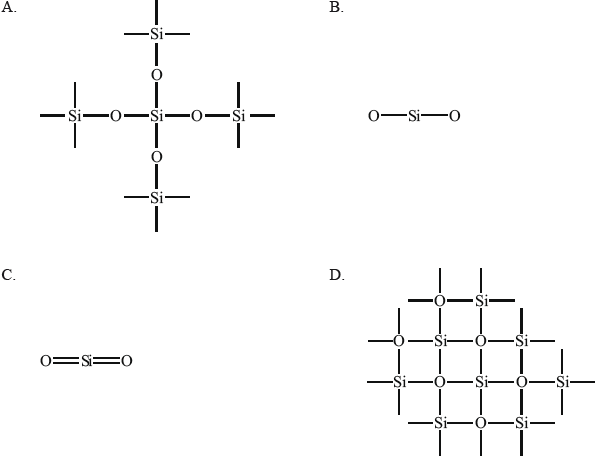
What describes the structure of silicon and silicon dioxide?

Which diagram represents the bonding in \({\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)?
Which change explains why the boiling points of the halogens increase as their molecular masses increase?
A. The intermolecular attraction due to temporarily induced dipoles increases.
B. The gravitational attraction between molecules increases.
C. The polarity of the bond within the molecule increases.
D. The strength of the bond within the molecule increases.
The formula of gallium phosphate is \({\text{GaP}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\). What is the correct formula of gallium sulfate?
A. \({\text{GaS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)
B. GaS
C. \({\text{G}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}\)
D. \({\text{G}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{S}}_{\text{3}}}\)
Which compound has a covalent macromolecular (giant covalent) structure?
A. MgO(s)
B. \({\text{A}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(s)}}\)
C. \({{\text{P}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\text{(s)}}\)
D. \({\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(s)}}\)
Which metal has the strongest metallic bond?
A. Li
B. Na
C. K
D. Rb
Which substance is made up of a lattice of positive ions and free moving electrons?
A. Graphite
B. Sodium chloride
C. Sulfur
D. Sodium
A substance has the following properties:
What is the most probable structure of this substance?
A. Network covalent
B. Polar covalent molecule
C. Ionic lattice
D. Metallic lattice
Which species contain a dative covalent (coordination or coordinate) bond?
I. Carbon monoxide, CO
II. Ammonia, \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
III. Oxonium ion, \({{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^ + }\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which molecule is non-polar?
A. \({\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{Cl}}\)
D. CO
What are the correct formulas of the following ions?
Which statement about the physical properties of substances is correct?
A. The only solids that conduct electricity are metals.
B. All substances with covalent bonds have low melting points.
C. Ionic solids are always brittle.
D. All metals have high densities.
Which molecule has a non-bonding (lone) pair of electrons on the central atom?
A. \({\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{Si}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}\)
What is the formula of magnesium fluoride?
A. \({\text{M}}{{\text{g}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{M}}{{\text{g}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{F}}\)
C. \({\text{M}}{{\text{g}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{Mg}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\)
Which statements about the structure and bonding of silicon dioxide are correct?

Which particles are responsible for electrical conductivity in metals?
A. Anions
B. Cations
C. Electrons
D. Protons
What are the correct formulas of the following ions?

What is the correct Lewis structure for hypochlorous acid, a compound containing chlorine, hydrogen and oxygen?
A. 
B. 
C. 
D. 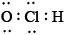
What is the correct order of increasing boiling points?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{I}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{I}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{I}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{I}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
What is the order of increasing boiling point?
A. C4H10 < CH3COOH < CH3CH2CHO < CH3CH2CH2OH
B. C4H10 < CH3CH2CHO < CH3CH2CH2OH < CH3COOH
C. CH3COOH < CH3CH2CH2OH< CH3CH2CHO < C4H10
D. C4H10 < CH3CH2CH2OH < CH3CH2CHO < CH3COOH
Metal M has only one oxidation number and forms a compound with the formula \({\text{MC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\). Which formula is correct?
A. \({\text{MN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{MN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\)
C. \({\text{MS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)
D. \({\text{MP}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)
Which is the correct Lewis structure for ethene?
Which order is correct when the following compounds are arranged in order of increasing melting point?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}} < {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}} < {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\)
B. \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}} < {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}} < {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} < {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}\)
D. \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}} < {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\)
Which molecules react to form a dative covalent (coordinate) bond?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\) and \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\) and \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\)
C. \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\) and HF
D. Cl2 and HF
Which combination of length and strength of the carbon‒to‒carbon bonds in \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\) and \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\) is correct?
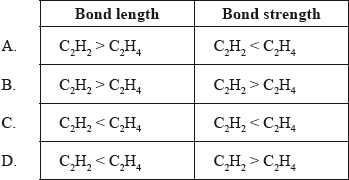
Which compound does not form hydrogen bonds between its molecules?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\)
What is the formula of magnesium nitride?
A. MgN
B. Mg2N3
C. Mg3N
D. Mg3N2
Which series shows increasing boiling points?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHO}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHO}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHO}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHO}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\)
The Lewis (electron dot) structure of paracetamol (acetaminophen) is:

What are the approximate values of the bond angles?

Which compounds have an ionic lattice structure in the solid state?
I. Silicon dioxide
II. Sodium fluoride
III. Ammonium nitrate
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which forces are present between molecules of carbon dioxide in the solid state?
A. Permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions
B. Temporary dipole-induced dipole interactions (London/dispersion forces)
C. Covalent bonding
D. Ionic bonding
Diamond, C60 fullerene and graphite are allotropes of carbon. Which statements are correct about these allotropes?
I. In diamond each carbon is held in a tetrahedral arrangement.
II. In C60 fullerene each carbon is held in a trigonal arrangement.
III. In graphite each carbon is held in a tetrahedral arrangement.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which compound has the shortest C–N bond?
A. CH3NH2
B. (CH3)3CNH2
C. CH3CN
D. CH3CHNH
Which combination of shape and bond angle best describes a molecule of sulfur dioxide, \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)?

What are the correct formulas of the following ions?
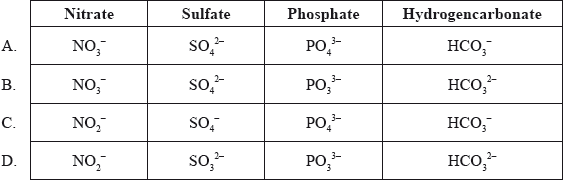
Which statement best describes ionic bonding?
A. It is the electrostatic attraction between positive ions and delocalized electrons and occurs by the transfer of electrons.
B. It is the electrostatic attraction between positive ions and negative ions and occurs by the transfer of electrons.
C. It is the electrostatic attraction between positive ions and negative ions and occurs by the sharing of electrons.
D. It is the electrostatic attraction between positive nuclei and electrons and occurs by the sharing of electrons.
How many bonding electrons are there in the urea molecule?
A. 8
B. 16
C. 20
D. 24
Which molecule contains a bond angle of approximately 120°?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\)
B. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)
C. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\)
D. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\)
Which two atoms form the most polar bond?
A. C and F
B. C and Cl
C. Si and F
D. Si and Cl
Between which pair of molecules can hydrogen bonding occur?
A. CH4 and H2O
B. CH3OCH3 and CF4
C. CH4 and HF
D. CH3OH and H2O
Which molecule has the shortest bond between carbon atoms?
A. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\)
B. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\)
C. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\)
What is the formula of calcium nitride?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{3}}}\)
C. \({\text{Ca(N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{Ca(N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\)
Which pair of molecules has the same bond angles?
A. PCl3 and BCl3
B. SO2 and CO2
C. H2O and NH3
D. CCl4 and SiH4
What are the approximate bond angles and structure of crystalline SiO2?
Which form of carbon is the poorest electrical conductor?
A. Graphite
B. Graphene
C. Diamond
D. Carbon nanotube
Which substance does not conduct electricity?
A. Solid zinc
B. Molten zinc
C. Solid zinc chloride
D. Molten zinc chloride
Which combination best describes the type of bonding present and the melting point of silicon and silicon dioxide?

What is the formula of the ionic compound formed when calcium and nitrogen react together?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{5}}}\)
Which statements concerning the sodium chloride ionic lattice are correct?
I. Sodium ions are larger than chloride ions.
II. Each sodium ion is surrounded by six chloride ions.
III. Each chloride ion is surrounded by six sodium ions.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
What is the molecular geometry and bond angle in the molecular ion NO3−?
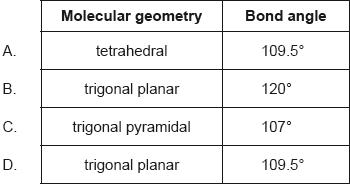
Which statements about graphite are correct?
I. Carbon atoms are held in layers with weak attractions between layers.
II. Graphite is a non-metal which conducts electricity.
III. Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to three other carbon atoms.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
What describes the relationship between diamond, graphite and \({{\text{C}}_{{\text{60}}}}\) fullerene?
A. Allotropes
B. Isomers
C. Isotopes
D. Polymers
What is the correct order of increasing boiling point?
A. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}} < {\text{HCHO}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH}}\)
B. \({\text{HCHO}} < {{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH}} < {\text{HCHO}} < {{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\)
D. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH}} < {\text{HCHO}}\)
How do the bond angles in \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\), \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\) and \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\) compare?
\(\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{\text{A.}}}&{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}}& = &{{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}}& = &{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \\ {{\text{B.}}}&{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}}& < &{{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}}& < &{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \\ {{\text{C.}}}&{{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}}& < &{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}}& < &{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}} \\ {{\text{D.}}}&{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}& < &{{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}}& < &{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}} \end{array}\)
What compound is formed when lithium reacts with selenium?
A. LiSe
B. \({\text{L}}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Se}}\)
C. \({\text{LiS}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{L}}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\)
Which properties do typical ionic compounds have?
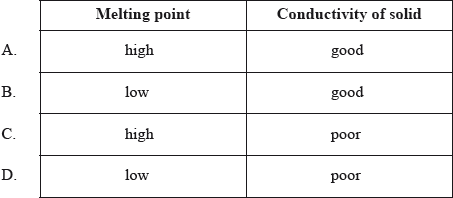
What is the formula of magnesium nitride?
A. \({\text{M}}{{\text{g}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{M}}{{\text{g}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\)
C. \({\text{Mg(N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{Mg(N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\)
Which substance can form intermolecular hydrogen bonds in the liquid state?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHO}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
Which particles are responsible for the conduction of electricity in molten aluminium?
A. Cations
B. Anions
C. Electrons
D. Protons
What are the predicted electron domain geometries around the carbon and both nitrogen atoms in urea, (NH2)2CO, applying VSEPR theory?
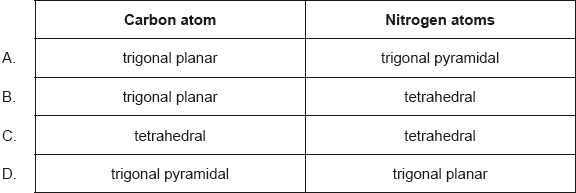
Which compound has the highest boiling point?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
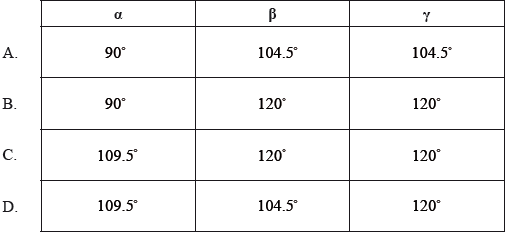
The Lewis (electron dot) structure of aspirin is represented below.

What are the approximate values of the bond angles \(\alpha \), \(\beta \) and \(\gamma \), in the molecule?
Which particles are present in the lattice of a metal?
A. Negative ions
B. Positive and negative ions
C. Positive ions
D. Molecules
Which statement best describes metallic bonding?
A. Electrostatic attractions between oppositely charged ions
B. Electrostatic attractions between a lattice of positive ions and delocalized electrons
C. Electrostatic attractions between a lattice of negative ions and delocalized protons
D. Electrostatic attractions between protons and electrons
The number of electrons in the valence shell of elements A and B, are 6 and 7 respectively. What is the formula and type of bonding in a compound formed by these elements?
A. \({{\text{A}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{B}}\), covalent
B. \({\text{A}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}\), covalent
C. \({{\text{A}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{B}}\), ionic
D. \({\text{A}}{{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}\), ionic
Which statement best describes the intramolecular bonding in HCN(l)?
A. Electrostatic attractions between \({{\text{H}}^ + }\) and \({\text{C}}{{\text{N}}^ - }\) ions
B. Only van der Waals’ forces
C. Van der Waals’ forces and hydrogen bonding
D. Electrostatic attractions between pairs of electrons and positively charged nuclei
Which statements are correct for the bonds between two carbon atoms?
I. Single bonds are longer than triple bonds.
II. Single bonds are stronger than double bonds.
III. Triple bonds are stronger than double bonds.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
What is the shape of the ammonia molecule, \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)?
A. Trigonal planar
B. Trigonal pyramidal
C. Linear
D. V-shaped (bent)
Which molecule is non-polar?
A. OF2
B. NH3
C. BF3
D. SO2
\({{\text{C}}_{{\text{60}}}}\) fullerene consists of a simple molecular structure. Silicon dioxide, \({\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\), can be described as a giant covalent (macromolecular) structure. Which statements are correct?
I. Each carbon atom in \({{\text{C}}_{{\text{60}}}}\) fullerene is bonded in a sphere of 60 carbon atoms, consisting of pentagons and hexagons.
II. Each O–Si–O bond angle in \({\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) is 180°.
III. \({\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) is insoluble in water.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which pair has the same bond angles?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ and NH}}_{\text{4}}^ + \)
B. \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ and }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\)
C. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ and }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ and S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)
Which process involves the breaking of hydrogen bonds?
A. \({\text{2HI(g)}} \to {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{C(g)}} + {\text{4H(g)}}\)
C. \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(l)}} \to {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\)
D. \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(l)}} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(g)}}\)
When \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\), \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\) and \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\) are arranged in order of increasing carbon-carbon bond strength (weakest bond first), what is the correct order?
A. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{, }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{, }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\)
B. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{, }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{, }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\)
C. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{, }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{, }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{, }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{, }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\)
What is the shape and the bond angle of the molecule \({\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\)?

Which species contains a bond angle of approximately 107°?
A. \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}\)
C. \({\text{NC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\)
D. \({\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\)
Which bond is the least polar?
A. C–H
B. F–H
C. O–H
D. N–H
What is the formula of calcium phosphide?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{3}}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{(P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}\)
Which of the following are van der Waals’ forces?
I. Dipole-dipole forces
II. Hydrogen bonds
III. London (dispersion) forces
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which is the best description of ionic bonding?
A. The electrostatic attraction between positively charged nuclei and an electron pair
B. The electrostatic attraction between positive ions and delocalized negative ions
C. The electrostatic attraction between positive ions and delocalized electrons
D. The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
Which single covalent bond is the most polar, given the following electronegativity values?

A. C–O
B. S–H
C. C–H
D. O–H
Which bonds are arranged in order of increasing polarity?
A. H–F \( < \) H–Cl \( < \) H–Br \( < \) H–I
B. H–I \( < \) H–Br \( < \) H–F \( < \) H–Cl
C. H–I \( < \) H–Br \( < \) H–Cl \( < \) H–F
D. H–Br \( < \) H–I \( < \) H–Cl \( < \) H–F
How many non-bonding pairs of electrons are there in a nitrogen molecule?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Which compound forms hydrogen bonds in the liquid state?
A. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}}\)
B. \({\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHO}}\)
D. \({{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}\)
The compounds shown below have similar relative molecular masses. What is the correct order of increasing boiling point?
A. CH3COOH < (CH3)2CO < (CH3)2CHOH
B. CH3COOH < (CH3)2CHOH < (CH3)2CO
C. (CH3)2CO < CH3COOH < (CH3)2CHOH
D. (CH3)2CO < (CH3)2CHOH < CH3COOH
Which compound contains both ionic and covalent bonds?
A. SIH4
B. NaNO3
C. H2CO
D. Na2S
Which of the following series shows increasing hydrogen bonding with water?
A. Propane < propanal < propanol < propanoic acid
B. Propane < propanol < propanal < propanoic acid
C. Propanal < propane < propanoic acid < propanol
D. Propanoic acid < propanol < propanal < propane
Which combination of the characteristics of element X, a metal, and element Y, a non metal, is most likely to lead to ionic bonding?

Which species contains a dative covalent (coordinate) bond?
A. HCN
B. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. CO
The following compounds have similar molar masses:
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH, C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH and C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]
What is the order of increasing boiling points?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}} < {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}\)
The electronegativity values of four elements are given.
What is the order of increasing polarity of the bonds in the following compounds?
A. CO < OF2 < NO < CF4
B. CF4 < CO < OF2 < NO
C. NO < OF2 < CO < CF4
D. CF4 < NO < OF2 < CO
Which bonds cause the boiling point of water to be significantly greater than that of hydrogen sulfide?
A. London (dispersion)
B. Covalent
C. Ionic
D. Hydrogen
Which diatomic molecule has the strongest bonding between its atoms?
A. \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)
B. \({{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\)
C. \({{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\)
Which compounds contain both ionic and covalent bonding?
I. \({\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\)
II. NaCl
III. NaOH
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
What is the formula of ammonium phosphate?
A. (NH3)3PO4
B. (NH4)3PO4
C. (NH4)2PO4
D. (NH3)2PO3
Which is the best description of the bonding present in silicon dioxide, \({\text{Si}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)?
A. Each silicon atom forms four single covalent bonds to oxygen atoms.
B. Each silicon atom forms two double covalent bonds to oxygen atoms.
C. Each silicon atom forms two single covalent bonds to oxygen atoms.
D. Each silicon atom forms four double covalent bonds to oxygen atoms.
Which species contain a dative covalent bond?
I. HCHO
II. CO
III. \({{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^ + }\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which molecule is polar?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\)
B. \({\text{BC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\)
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}\)
Which row correctly describes the bonding type and melting point of carbon and carbon dioxide?

Which species has the longest carbon to oxygen bond length?
A. CO
B. CH3OH
C. CH3CO2−
D. H2CO
Which compound has resonance structures?
A. C6H12
B. CH3CHO
C. NaBr
D. Na2CO3
Which statement is correct about carbon-oxygen bond lengths?
A. The C–O bond lengths are equal in propanoic acid, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{COOH}}\).
B. The C–O bond length in carbon dioxide, \({\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\), is longer than the C–O bond length in methanol, \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH}}\).
C. The C–O bond length in carbon dioxide, \({\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\), is longer than the C–O bond length in carbon monoxide, CO.
D. The C–O bond lengths are equal in ethyl ethanoate, \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COO}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\).
What are the strongest intermolecular forces between molecules of propanone, CH3COCH3, in the liquid phase?
A. London (dispersion) forces
B. Covalent bonding
C. Hydrogen bonding
D. Dipole–dipole forces
Which of the following does not react with dilute HCl(aq)?
A. Na2CO3
B. Cu
C. Zn
D. CuO
Which correctly states the strongest intermolecular forces in the compounds below?
Which substance has a giant covalent structure?
Which combination describes the sulfate(IV) ion, SO32– (also known as sulfite ion)?